As we all know, when the parasite eggs will not die when they go through winter. When the temperature rises in spring, it’s the best time for parasite eggs to grow. Therefore, the prevention and control of parasites in spring is particularly difficult. At the same time, cattle and sheep are lacking of nutrients after going through the cold hay season, and the parasites aggravate the consumption of nutrients in animals, which lead to poor physical fitness of cattle and sheep, weak disease resistance, and body weight loss.
Deworming workflow and precautions:
1. Before deworming, check the health status of the cattle and sheep: Mark the seriously ill cattle and sheep, suspend deworming and isolate, and deworm after recovery. Reduce stress response during the treatment of other diseases in cattle and sheep, while avoiding the interaction between different drugs.
2. Deworming is carried out purposefully and pertinently, distinguish all types of parasites to be dewormed: there are many parasites in cattle, for example, Ascaris, Fasciola hepatica, tapeworm, bovine lice, bovine tick, bovine scabies mites, bovine eperythropoiesis, etc. It is necessary to judge the type of parasites according to clinical symptoms, so as to deworm them in a targeted manner.
3. During the deworming period, the excrement should be concentrated: by accumulating heat, removing the parasite eggs, and reducing the probability of re-infection of the animals. the deworming effect of many farms is not good because the excrement are not concentrated and accumulated, resulting in secondary infection.
4. During the deworming period, do not cross-use excrement disposal tools: The production tools in the dewormed breeding area cannot be used in the non-dewormed breeding area, nor can they be used in the feed stacking area. Avoid cross-contamination of parasite eggs in different enclosures and cause infection.
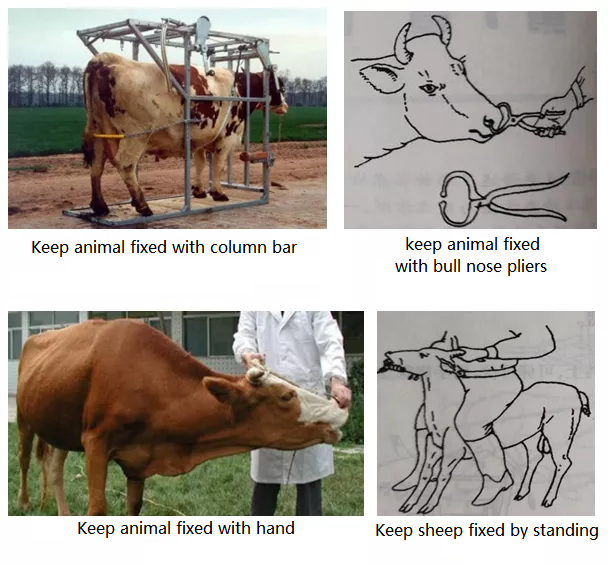
5. The cattle and sheep are not properly secured and the injection is not in place: the subcutaneous injection and the intramuscular injection are confused, resulting in an unsatisfactory deworming effect. Fixed protection is the basic operation before injecting liquid medicine into animals to avoid leakage of needles, bleeding needles, and ineffective needles. To fix and protect cattle and sheep, you need to prepare restraint tools such as rope sets and nose pliers in advance. After fixing the uncooperative cattle and sheep, then can deworm them. At the same time, we could prepare an opaque black cloth to cover the eyes and ears of cattle and sheep,to reduce excessive behavior of cattle and sheep;
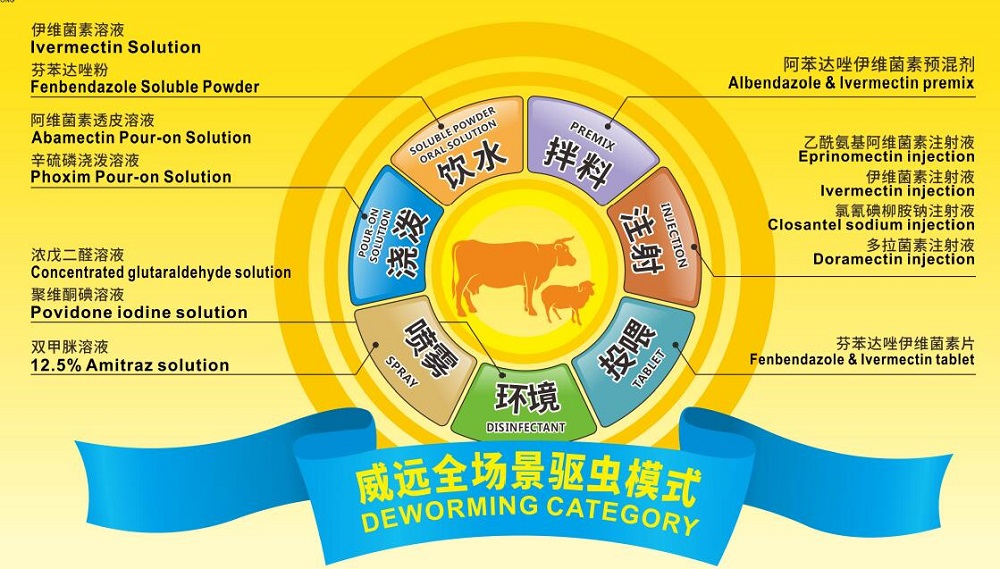
6. Choose the anthelmintic drugs correctly and be familiar with the properties of the drugs:In order to achieve better anthelmintic effect, broad-spectrum, high-efficiency and low-toxic anthelmintic drugs should be used. Be familiar with the medicinal properties, safety range, minimum poisoning dose, lethal dose and specific rescue medicine of the anthelmintic drugs used.
7. It is best to deworm in the afternoon or evening: because most cattle and sheep will excrete worms during the day on the second day, which is convenient for excrement collection and disposal.
8. Do not deworm during the feeding process and one hour after feeding: avoid affecting the normal feeding and digestion of animals; after feeding, animals will be full of stomach, so as to avoid mechanical stress and damage caused by fixing cattle and sheep.
9. Incorrect administration method:
Medications that should be injected subcutaneously are injected into the muscle or intradermally with poor results. For cattle, the correct subcutaneous injection site can be selected on both sides of the neck; for sheep, the injection site can be subcutaneously injected on the side of the neck, the dorsal ventral side, the back of the elbow, or the inner thigh. When injecting, the needle is inclined upward, from the fold at the base of the fold, at 45 degrees to the skin, and pierces two-thirds of the needle, and the depth of the needle is appropriately adjusted according to the size of the animal. When using oral anthelmintics, farmers will mix these anthelmintics into the concentrate for feeding, which will cause some animals to eat more and some animals to eat less, resulting in poor deworming effect.
10. Leaking liquid, and failing to make up injections in time: this is a common factor that affects the effect of deworming. When giving injections to animals, it is necessary to make up injections and make up liquid medicines for any situations such as bleeding and leaking liquids, etc. The amount depends on the amount of leakage, but it must be replenished in time.
11. Set the deworming program and deworm regularly:
Making a deworming program, and conduct deworming regularly according to the established deworming program, and keep a record of deworming, which is easy to query and facilitates the prevention and control of parasites; repeat deworming to ensure the deworming effect: In order to achieve a better deworming effect, After 1-2 weeks of deworming, carry out a second deworming, the deworming is more thorough and the effect is better.
Deworm large groups twice a year, and take larval deworming techniques in spring. Deworming in the fall prevents the emergence of adults in the fall and reduces the outbreak of larvae in the winter. For areas with severe parasites, deworming can be added once during this period to avoid ectoparasitic diseases in winter and spring.
Young animals are generally dewormed for the first time in August-September of the year to protect the normal growth and development of lambs and calves. Additionally, pre- and post-weaning pups are susceptible to parasites due to nutritional stress. Therefore, protective deworming is required at this time.
Prenatal deworming of dams close to parturition avoids fecal helminth egg “postpartum elevation” at 4-8 weeks postpartum. In areas with high parasite contamination, dams must be dewormed 3-4 weeks postpartum.
For cattle and sheep purchased from outside, deworming is performed once 15 days before entering the mixed flock, and deworming is performed once before transferring or turning circles.
12. When deworming, do a small group test first: after there is no adverse reaction, conduct a large group deworming.
Post time: Mar-09-2022


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)