Overview of the development of the epidemic in Vietnam
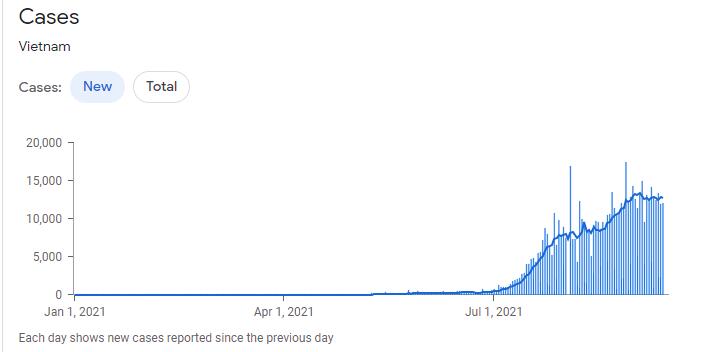
The epidemic situation in Vietnam continues to deteriorate. According to the latest news from the Ministry of Health of Vietnam, as of August 17, 2021, there were 9,605 newly confirmed cases of new coronary pneumonia in Vietnam on that day, of which 9,595 were local infections and 10 were imported cases. Among them, the new confirmed cases in Ho Chi Minh City, the “epicenter” of the southern Vietnam epidemic, accounted for half of the new cases nationwide. Vietnam’s epidemic has spread from Bac River to Ho Chi Minh City and now Ho Chi Minh City has become the hardest hit area. According to the health department of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, more than 900 front-line anti-epidemic medical personnel in Ho Chi Minh City have been diagnosed with the new crown.
01 Vietnam’s epidemic is fierce, 70,000 factories closed in the first half of 2021
According to a report by “Vietnam Economy” on August 2, the fourth wave of epidemics, mainly caused by mutant strains, is fierce, leading to the temporary closure of a number of industrial parks and factories in Vietnam, and the interruption of production and supply chains in various regions due to the implementation of social quarantine, and the growth of industrial production Slow down. The 19 southern provinces and municipalities directly under the Central Government implemented social distancing in accordance with the government’s instructions. Industrial production fell sharply in July, of which the industrial production index of Ho Chi Minh City fell by 19.4%. According to the Ministry of Investment and Planning of Vietnam, in the first half of this year, a total of 70,209 companies in Vietnam closed down, an increase of 24.9% over last year. This is equivalent to roughly 400 companies closing down every day.
02 The manufacturing supply chain has been hit hard
The epidemic situation in Southeast Asia continues to be acute, and the number of new crown pneumonia infections has surged again. The Delta mutant virus has caused chaos in factories and ports in many countries. In July, exporters and factories were unable to maintain operations, and manufacturing activities fell sharply. Since the end of April, Vietnam has seen a surge of 200,000 local cases, more than half of which are concentrated in the economic center of Ho Chi Minh City, which has dealt a severe blow to the local manufacturing supply chain and forced international brands to find alternative suppliers. The “Financial Times” reported that Vietnam is an important global apparel and footwear production base. Therefore, the local epidemic has disrupted the supply chain and has a wide range of impacts.
03 The suspension of production at a local factory in Vietnam caused a “supply cut” crisis
Due to the impact of the epidemic, Vietnam’s foundries are close to “zero output”, and local factories have stopped production, causing a “supply cut” crisis. Coupled with the high import demand of American importers and consumers for Asian goods, especially Chinese goods, the problems of port congestion, delivery delays, and space shortages have become more serious.
The US media recently warned in reports that the epidemic has brought difficulties and impacts to American consumers: “The epidemic has caused factories in South and Southeast Asia to stop production, increasing the risk of disruption in the global supply chain. US consumers may soon find local The shelves are empty”.
Post time: Sep-14-2021


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)